BioCell Collagen for joint, skin and connective tissue healthBioCell Collagen for joint, skin and connective tissue health
BioCell Collagen is a healthy aging ingredient that promotes joint health and skin beauty.
April 17, 2018

Sponsored Content
Intrinsic aging produces many physiological changes that affect how the body looks and feels which depends, at least in part, upon the structural integrity of the connective tissue in joints, skin, tendons, ligaments, bones and blood vessels. Connective tissue, which is primarily composed of collagen, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), and proteoglycans, binds all of the organs and other tissues of the body. Aging gradually weakens the connective tissue by depleting collagen and GAG accumulation, and by UV initiated photo-damage and other lifestyle risk factors such as smoking or chronic exposure to environmental pollutants.
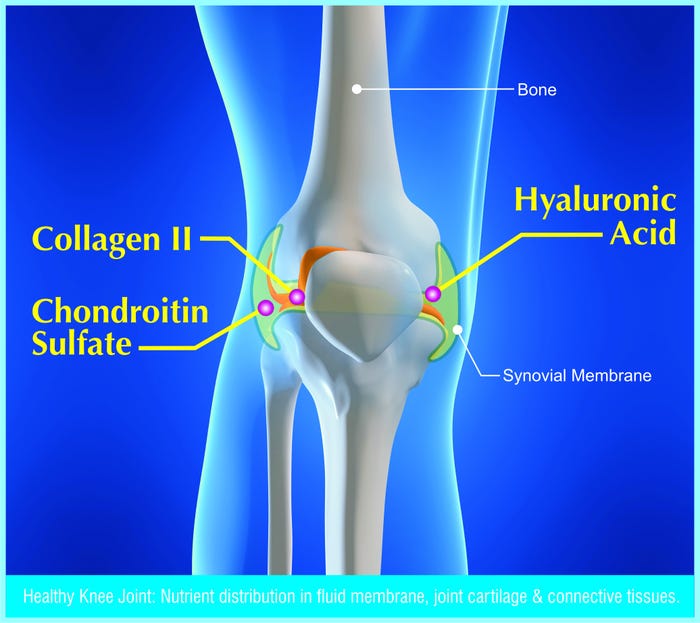
Nutraceuticals have been used for several decades to ameliorate the physiological degradation of connective tissue, associated with a decline in skin firmness and elasticity, and joint comfort and mobility due to aging. Among these nutraceuticals is branded healthy aging dietary supplement ingredient called BioCell Collagen® developed and distributed by BioCell Technology, LLC of Irvine, Calif. Multiple human clinical trials including safety, efficacy and bioavailability studies have demonstrated that oral ingestion of BioCell Collagen promotes joint health and skin beauty.
BioCell Collagen is a novel hydrolyzed chicken sternal cartilage extract composed of collagen type II peptides, chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid in a highly absorbable matrix form.
A comprehensive approach to healthy aging
Many internal and external factors influence the pace and effects of aging. The progression of aging is linked to steady deterioration of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in connective tissue, which results from decreased synthesis and increased degradation of molecules essential for connective tissue integrity.
Because collagen and GAGs such as chondroitin sulfate (CS) and hyaluronic acid (HA) are the major molecular constituents of the ECM, their replenishment could help counteract various undesirable effects of aging. These effects include overall bodily weakness, vulnerability to injury and visible facial changes. However, there are very few science-backed dietary supplements on the market that address the loss of these structurally essential molecules. BioCell Collagen comprehensively addresses the loss of these molecules by providing both collagen and GAGs.
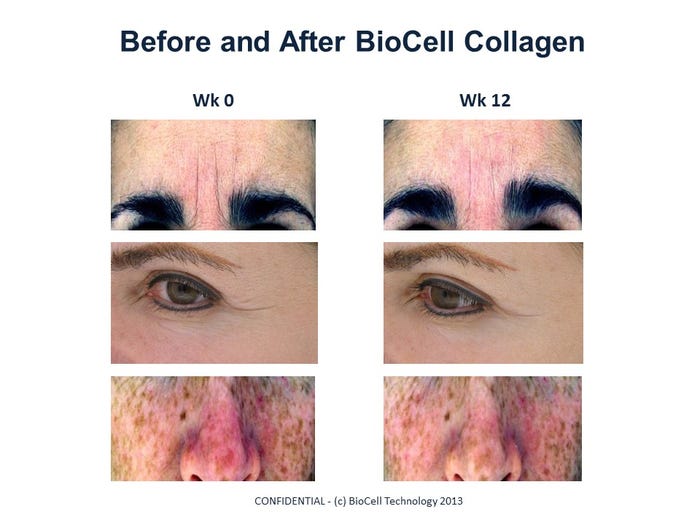
Disclaimer: BioCell Collagen supplementation 1 g per day for 12 weeks. Results not typical, individual results may vary.
The unique molecular nature of BioCell Collagen
BioCell Collagen is derived exclusively from hormone and antibiotic-free chicken sternal cartilage, which is a rich source of type II collagen, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate, and closely mirrors the composition of human articular cartilage. Cartilage is a very clean and desirable source because it is free from blood supply and it is devoid of lymphatics, blood vessels and nerves, unlike other animal parts (e.g., cow or pig skin and bones) from which most collagen ingredients are derived. The source is of importance because many impurities are carried through the blood supply, thus obtaining exclusively from cartilage eliminates the risk of potential contamination. In the dietary supplement industry, when collagen is marketed without denoting the type, it usually means the collagen product is made of types I and III collagen, also known as gelatin. Collagen types I and III coexist in skin and bone tissues. Collagen type II is rare and more valuable because it is predominantly found in cartilage where it naturally coexists with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate in a blood-free environment.
BioCell Collagen is manufactured via a patented procedure that includes filtration, purification, concentration, hydrolysis and sterilization to ensure consistent quality and safety. This process reduces the size of its molecules to a specific range thereby increasing the bioavailability of the bioactive constituents found within the unique biomolecular composition of BioCell Collagen. The synergy among BioCell Collagen’s three biomolecular matrix constituents are unique and cannot be found in any other collagen ingredients or blends.
The scientific studies of BioCell Collagen
The ingestion of BioCell Collagen is thought to stimulate chondrocytes and play a role in the renewal mechanism of cartilage and to stimulate fibroblasts for skin renewal, thus supporting all three major collagen types (I, II and III). Moreover, BioCell Collagen was shown to have a concentration-dependent inhibition of hyaluronidase, the enzyme that degrades hyaluronic acid, which can contribute to signs of aging on the skin and loss of viscoelasticity of joint synovial fluid. BioCell Collagen also attenuates deleterious changes in inflammatory biomarkers including creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and C-reactive protein adding further clues into its mechanism of action.
In an 80 subject, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 2 grams of BioCell Collagen were taken daily for 12 weeks to promote joint health. The subjects experienced statistically significant improvements in their ability to engage in physical activities (Schauss et al., 2012). These results corroborated the results of an earlier double-blind placebo-controlled trial tested on 16 people. (Kalman et al., 2004).
In another randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of BioCell Collagen, healthy, recreationally active subjects were given three grams of BioCell Collagen over a six-week period before an upper-body muscle-damaging resistance exercise challenge. Participants experienced favorable improvements in stress resilience and recovery after bouts of intense resistance exercise without any reported side effects (Lopez et al, 2014).
A pilot clinical study on BioCell Collagen showed that a daily intake of one gram of BioCell Collagen significantly reduced skin dryness and facial wrinkles in association with an increase in blood circulation and collagen content in the skin. (Schwartz and Park, 2012).
Skin beauty
Clinically shown to:
Reduce fine lines and wrinkles
Reduce skin dryness/scaling
Increase collagen content in the dermis
Increase blood microcirculation of facial skin
Joint support
Clinically shown to:
Improve joint comfort and mobility
Impact key biochemical markers of connective and skeletal muscle tissue damage and enhance stress resilience following intense resistance exercise

You May Also Like



